
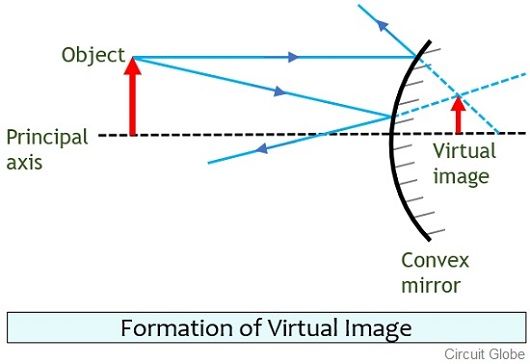
The backward extension of refracted or reflected light rays is true for a virtual image that is, it doesn't exist in reality.įor a convex lens, placing an object at or near a distance equal to or less than the focal length will give you a real image.

When the light rays after refraction or reflection meet at a point, it exists in reality, meaning a real image can be placed on the screen. Space is not the same as from the object to the lenses.

As the object nears the focal point, the image will move towards infinity, and when the object surpasses the focal point, the image becomes virtual and is upright. When rays converge, real image occurs, and when rays only appear to diverge, virtual image occurs.īy usage of concave mirrors and converging lenses, a real image can be produced, but on the condition that the object placed further away from the mirror/lens than the focal point, and the real image is inverted. In simplistic terms, an image located in the plane of convergence for the light rays emitted from an object known as a real image. An assortment of focus points made by the converging rays is known as a real image, whereas the collection of focus points made by the extension of diverging rays is known as the virtual image. Some of these rays which represent the light reach the mirror's surface and reflect off the surface as per the laws of reflection.Ī compilation of focus points of light rays emitting from an object defined as an image in terms of optics. The word object in the definition can be anything that emits light rays.Īs light is emanating from an object in a variety of directions, an image is formed. Image – When the light rays coming from an object appear to meet at a point after reflection or refraction, the point may be defined as an image.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
